What Defines a Lease Agreement in Texas?
In Texas, a lease agreement outlines rights and duties for landlords and tenants. A written agreement is mandatory for a lease longer than a year. However, even short-term rentals should have a lease to protect your legal rights.
Texas lease agreements should include:
- Landlord’s name, address, phone number, and tenant contact information.
- Length of the lease agreement, renewal policies, and rent increase details.
- Rent amount, due date, and methods for payment of rent.
- Late rent fees, grace periods, and any recurring fees (e.g., parking).
- Security deposit details for the amount, deductions, and return process.
- Responsibilities for repairs, maintenance, and utilities.
- Penalties for breach of lease terms a clear eviction process.
- Disclosures for lead-based paint hazards and electric service interruption.
After a lease ends, Texas landlords should give tenants a copy of the lease agreement within three days to avoid any disputes if they can’t find the original.
You can create a free Texas Lease Agreement and have it e-signed using Baselane.
Rights & Responsibilities
Texas landlord tenant laws apply to any rental agreement (either spoken or written). These laws are outlined in the TX Property Code Chapter 92.
Texas Landlord Rights & Responsibilities
Rights:
- Screen potential tenants and require documentation.
- Collect the agreed-upon rent amount on the due date.
- Enforce penalties or evictions for lease violations.
Responsibilities:
- Ensure the property is in habitable condition.
- Address repair requests in a timely manner.
- Don’t engage in retaliatory action for violation of lease terms.
Texas Tenant Rights & Responsibilities
Rights:
- Live in a safe and functional property.
- Terminate a lease early for unsafe living conditions.
- Reside in an environment free from discrimination.
Responsibilities:
- Pay rent on time, as agreed.
- Keep the unit in good condition.
- Give reasonable notice before vacating.
Screening Tenants
Texas laws allow landlords to use the following selection criteria for choosing tenants:
- Income
- Criminal history
- Rental history
- Credit history
Tenant selection criteria must be in writing and signed by applicants. Ensure tenant screening follows Fair Housing Act rules that prohibit discrimination based on color, race, gender, religion, familial status, sexual orientation, disability, and more.
Maintenance and Repairs
Texas Property Code Section 92.056(b) requires landlords to handle repairs that impact tenant health or safety. It’s important to outline policies and timelines for maintenance and repairs in your rental agreement.
Landlord Responsibilities:
- Address repairs within 7 days of being notified.
- Maintain the property according to building, housing, or health codes.
Tenant Responsibilities:
- Notify landlords of maintenance issues or repair requests in writing.
- Use rental property fixtures appropriately, reporting any malfunctions.
- Dispose of waste regularly, at least once a week.
Entry Laws
You have the right to enter your tenant’s rental unit with adequate notice to make repairs and updates or replacements as required by law (e.g., smoke alarms). There’s no specified amount of time, but 24-hour’s notice is generally considered reasonable. In an emergency, you can enter the unit without notice. You must provide tenants with a written record of your visit.
Providing Utilities
- Bills: According to Texas landlord tenant laws, you must provide functional facilities if you charge for utilities, like electricity, water, or gas.
- Shutoffs: You can’t turn off utilities if tenants pay utility companies directly or in retaliation for nonpayment of rent.
- Disruptions: Legitimate reasons for utility disruptions include repairs, construction, or an emergency.
- Nonpayment: If utilities are shut off because you failed to pay the utility bill, tenants can take legal action.
- Restoration: Unlawful utility disconnection can result in a court order for the to reconnect the service.
Texas Rent Payments
- Rent Increase: Texas doesn’t have any rent control laws or regulations to provide notice before increasing rent.
- Late Payments: State laws allow a two-day grace period before collecting late fees. The maximum limit is 12% for properties with 1-4 units and 10% for properties with five or more units.
- Rent Withholds: Tenants can’t withhold rent under the “Repair and Deduct” right unless the damages affect their physical health.
- Cash Payments: If rent is paid in cash, a receipt is needed. For other payment methods, receipts are optional but always recommended.
Security Deposits Clauses
- Amount: There are no security deposit limits in Texas, although some counties may have specific security deposit laws.
- Deductions: Texas allows security deposit deductions for property damages outside of normal wear and tear. A list of deductions must be provided to the tenant.
- Returns: Landlords have 30 days for the return of security deposits after a tenant moves out.
- Penalties: Security deposit funds can’t be withheld without good reason, or you might owe the tenant three times the withheld amount and potentially their lawyer fees.
- Disputes: For security deposit disputes, it’s on you as the landlord to prove that keeping part of the deposit was the right call.
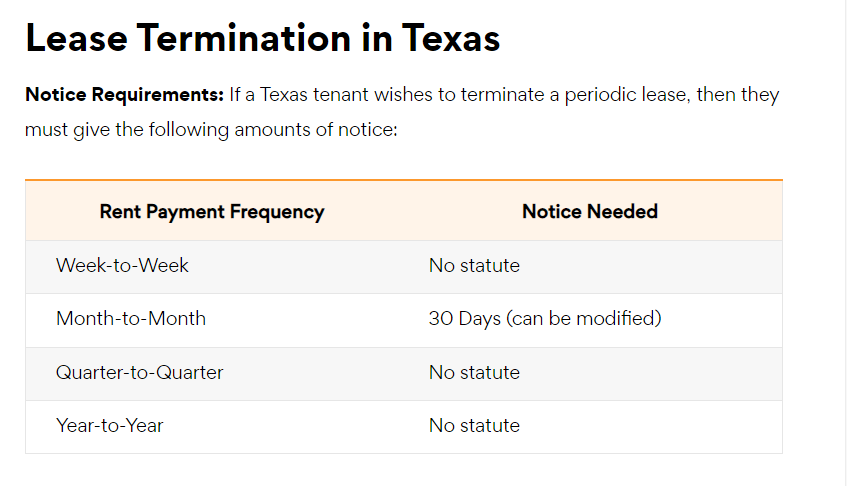
Lease Termination and Eviction Rules
- Lease Termination: Landlords can end a tenancy early for violating lease terms, engaging in illegal activities, or if the property undergoes foreclosure.
- Providing Notice: Texas landlord tenant laws state that landlords must send a written notice to vacate three days before starting the eviction process.
- Eviction Lawsuits: If a tenant doesn’t move out after receiving notice, you can file for eviction with the court (also known as a forcible entry and detainer suit).
- Getting Possession: If successful in your action, the tenant can be forcibly evicted by law enforcement 24 hours after receiving a court order to vacate the property (called a Writ of possession).
Final Thoughts
Texas landlord-tenant laws provide a solid foundation for lease agreements and a positive rental experience. Using the right property management tools can help keep you compliant.
Baselane offers solutions tailored for landlords to help handle rent payments, late fees, security deposits, lease agreements, and more. Book a FREE Demo today.







